Polypropylene is one of the most widely used polymers in the world, found in everything from packaging materials to textiles and automotive components. Its versatility, affordability, and durability make it indispensable in modern industries. In this blog post, we will explore polypropylene in detail, starting with its Lewis structure representation, chemical properties, and its practical applications. This post is designed to be both informative and SEO-friendly, ensuring readers gain value while search engines recognize its relevance.
What is Polypropylene?
Polypropylene (PP) is a thermoplastic polymer produced through the polymerization of propene (C3H6), a simple hydrocarbon. It belongs to the polyolefin group of polymers and is widely valued for its chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and lightweight nature. Polypropylene is extensively used in packaging, textiles, automotive parts, and medical devices.
Polypropylene’s properties and structure originate from its repeating unit, derived from propene molecules. Before delving into its applications, let us first understand the Lewis structure of its building block.
Breaking Down the Lewis Structure of Polypropylene
While a polymer like polypropylene does not have a single definitive Lewis structure, understanding its monomer unit helps us interpret its molecular structure.
1. The Monomer Unit: Propene (C3H6)
Propene, also called propylene, is the building block for polypropylene. Its chemical formula is C3H6, and its Lewis structure can be represented as:
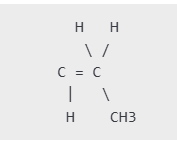
- The first two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond (C=C).
- The second carbon is attached to a methyl group (CH3) and a single hydrogen atom.
In the propene molecule:
- The double bond represents unsaturation, which is crucial for polymerization.
- The Lewis structure illustrates how valence electrons are shared to form covalent bonds between atoms.
2. Polymerization of Propene to Form Polypropylene
During the polymerization process, the double bond in propene breaks, allowing the monomers to link together through single covalent bonds. This reaction is called addition polymerization. The resulting structure is a repeating unit of the form:
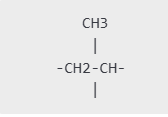
- Here, the methyl group (CH3) is attached to every alternate carbon atom in the polymer chain.
- The polymer chain consists of single bonds, making polypropylene stable and resistant to chemical breakdown.
- The letter n indicates the number of repeating units, which can vary depending on the desired polymer properties.
Properties of Polypropylene
Polypropylene owes its widespread use to a range of desirable properties:
1. Chemical Resistance
Polypropylene is resistant to many chemicals, including acids, bases, and organic solvents. This property makes it suitable for chemical containers and laboratory equipment.
2. Lightweight
PP has a low density (around 0.90 g/cm³), making it an ideal material for lightweight products such as packaging and automotive components.
3. High Tensile Strength
Polypropylene is mechanically strong and durable, which allows it to withstand stretching and pulling forces without breaking.
4. Heat Resistance
It has a high melting point (around 160°C), which enables it to withstand high-temperature applications without deforming.
5. Non-Toxic and Safe
Polypropylene is food-safe and widely used in food storage containers, baby bottles, and kitchenware.
6. Recyclable
PP is highly recyclable, contributing to sustainable product development.
Applications of Polypropylene
Due to its exceptional properties, polypropylene is used across multiple industries. Below are some of its most common applications:
1. Packaging Industry
Polypropylene is extensively used in food packaging, plastic containers, films, and bags due to its lightweight nature and moisture resistance. Flexible packaging materials like BOPP films (biaxially oriented polypropylene) are widely used in snack packaging.
2. Textile Industry
PP is a key material in the production of fibers for carpets, ropes, and thermal clothing. It is also used to manufacture non-woven fabrics for face masks, hygiene products, and medical gowns.
3. Automotive Industry
The automotive sector relies on polypropylene for interior parts, bumpers, and battery casings. Its strength-to-weight ratio ensures durability without adding unnecessary weight to vehicles.
4. Medical and Healthcare
Polypropylene’s non-toxic and sterilizable nature makes it ideal for medical devices, syringes, and laboratory containers.
5. Consumer Products
From furniture and storage containers to reusable water bottles and stationery items, polypropylene finds its way into a variety of everyday products.
6. Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, polypropylene is used for pipes, chemical tanks, and components exposed to harsh chemicals.
Why Polypropylene is Popular: Key Benefits
To summarize, polypropylene is popular because it offers:
- Cost-effectiveness: Affordable production and lightweight properties.
- Versatility: Suitable for multiple applications, from packaging to medical products.
- Durability: High strength and resistance to wear, chemicals, and heat.
- Sustainability: Recyclable, reducing environmental impact.
These benefits make polypropylene an ideal choice for manufacturers looking to balance performance and cost-efficiency.
Environmental Impact of Polypropylene
While polypropylene is recyclable, improper disposal of plastic products can lead to environmental pollution. Here are some key points regarding its environmental impact:
- Recycling Opportunities: Polypropylene is classified as Plastic #5, which is recyclable in many municipal programs.
- Energy Efficiency: PP production requires less energy compared to other plastics.
- Pollution Challenges: If not recycled, polypropylene contributes to plastic waste in landfills and oceans.
To address these challenges, industries are developing biodegradable alternatives and improving recycling technologies.
Conclusion: The Role of Polypropylene in Our Daily Lives
Polypropylene is an exceptional polymer that balances performance, cost, and sustainability. While it may not have a single definitive Lewis structure, understanding its molecular composition and polymerization process provides insights into its strength and versatility. From food packaging and textiles to medical devices and automotive components, polypropylene continues to play a vital role in shaping modern life.
As the demand for sustainable materials grows, polypropylene’s recyclability and durability make it a frontrunner in creating a greener future.